


The housing market in 2025 has demonstrated an unexpected resilience, primarily due to the favorable behavior of mortgage spreads. Despite recent inflationary trends indicated by producer and consumer price indices, mortgage rates have largely held steady, preventing the significant increases that would typically accompany such economic shifts. This stability, attributed to improved mortgage spreads, has proven to be a crucial shock absorber for the housing sector, mitigating the potential for demand to falter under higher borrowing costs. The ongoing performance of these spreads suggests a more positive outlook for housing affordability, even in the face of fluctuating economic indicators.
Detailed Analysis of Housing Market Dynamics
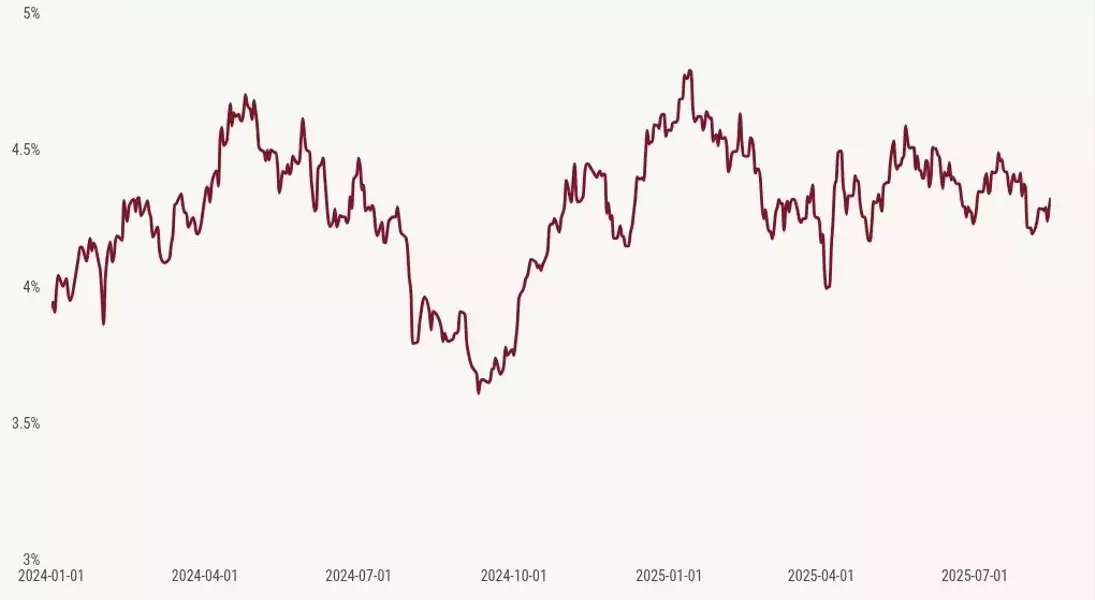
In the financial landscape of 2025, the stability of mortgage rates has emerged as a beacon for the housing market, defying the implications of hotter-than-anticipated inflation figures. Last week, despite the release of a robust Producer Price Index (PPI) report and a core Consumer Price Index (CPI) showing a 3.1% year-over-year increase, mortgage rates remained surprisingly consistent. This remarkable steadiness can be attributed to a significant improvement in mortgage spreads, which have acted as a crucial buffer. Historically, such inflation data would have propelled mortgage rates considerably higher, potentially adding 0.70% to 0.80% to current levels had 2023's less favorable spreads persisted.
The impact of improved mortgage spreads in 2025 cannot be overstated, as their positive influence on housing demand often goes unnoticed. Had these spreads not strengthened from their challenging 2023 levels, the real estate market would undoubtedly face more severe demand contractions. Forecasts for 2025 anticipated a 0.27% to 0.41% improvement in these spreads from their 2024 average of 2.54%. While this target is nearly met, the continued trend suggests a more stable borrowing environment. This was vividly illustrated last week when, despite an aggressive climb in bond yields, better mortgage spreads contained the upward pressure on mortgage rates. In stark contrast, similar scenarios in 2023 and 2024 would have seen rates escalate significantly from the outset of the week.
If mortgage spreads were to revert to their 2023 peak, current mortgage rates would surge by approximately 0.80%. Conversely, a return to the historical normal range of 1.60% to 1.80% would see rates drop by 0.50% to 0.70%. Achieving the best historical spread levels could push today's mortgage rates down to an appealing 5.88% to 6.08%.
In the 2025 outlook, mortgage rates were projected to oscillate between 5.75% and 7.25%, with the 10-year Treasury yield expected to fluctuate between 3.80% and 4.70%. Last week, the hotter PPI report indeed pushed bond yields up, reaching 4.30% before settling at 4.32%. However, mortgage rates, which began the week at 6.58%, only saw minor fluctuations, dipping to 6.53% before returning to 6.58%. This demonstrates the current resilience of mortgage rates, a novel experience for many, driven by the improving mortgage spreads. The market no longer requires a sub-4% 10-year yield to achieve near 6% mortgage rates; a yield closer to 4% with enhanced spreads now suffices.
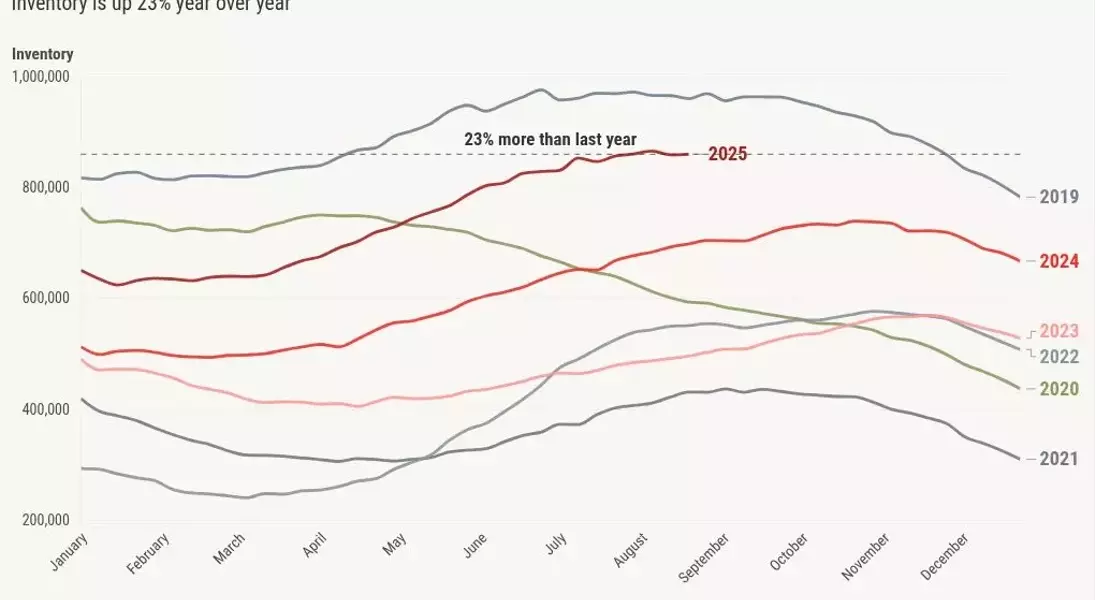
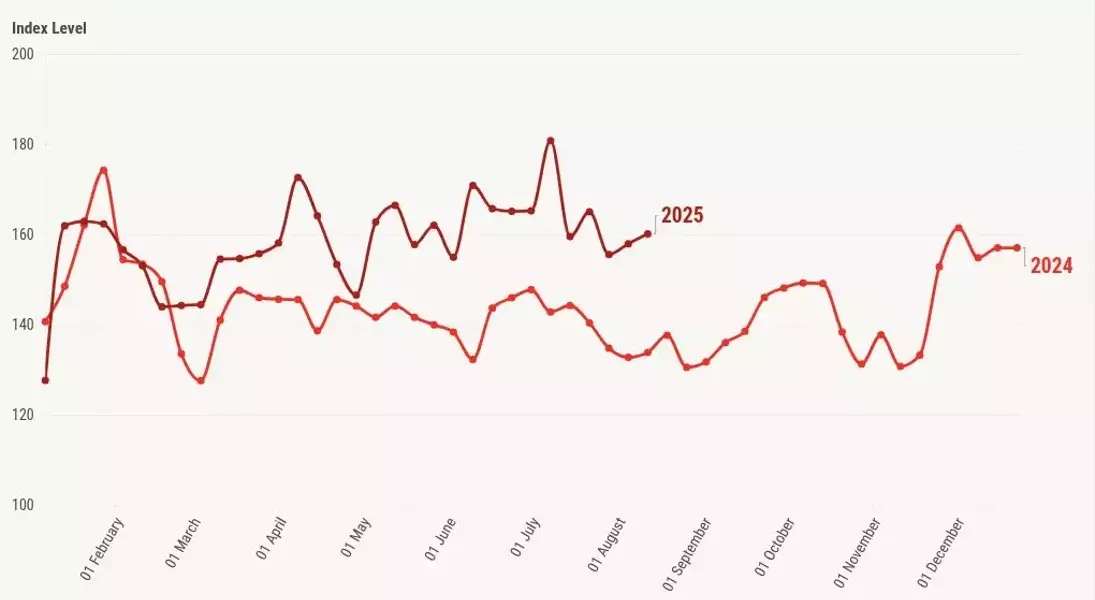
Regarding housing inventory, a surprising dip occurred two weeks ago, with stabilization observed towards mid-to-late June. While an inventory reduction in early August is uncommon, it was more prevalent pre-COVID. Inventory rose minimally last week, from 859,096 to 860,068 units, compared to 692,833 to 698,161 units in the same week last year. Year-over-year inventory growth has moderated from 33% to 23%, indicating a positive trend for housing even without rates nearing 6%.
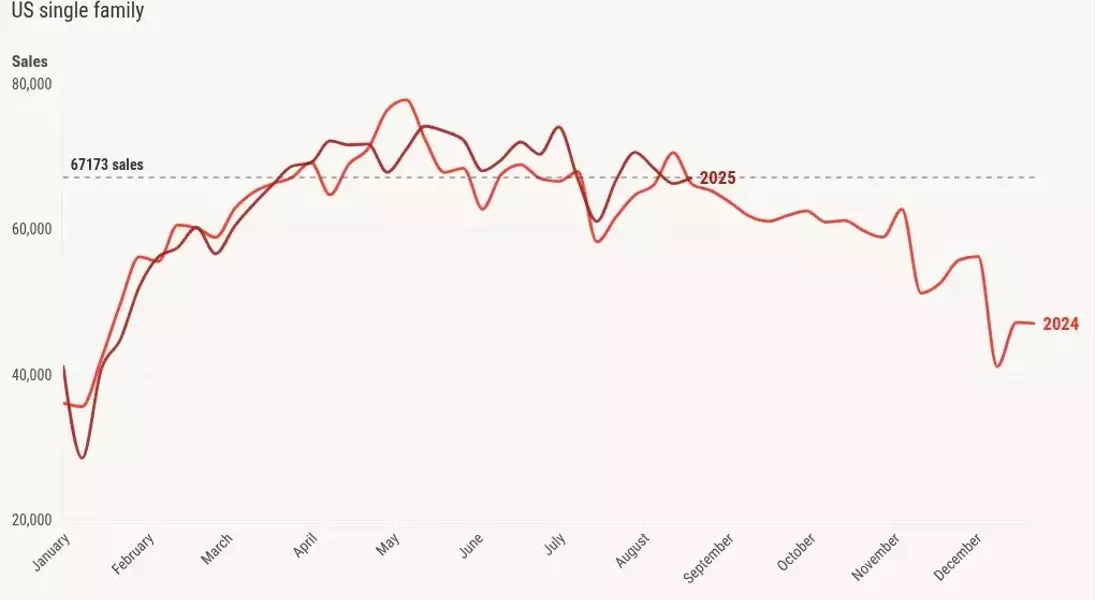
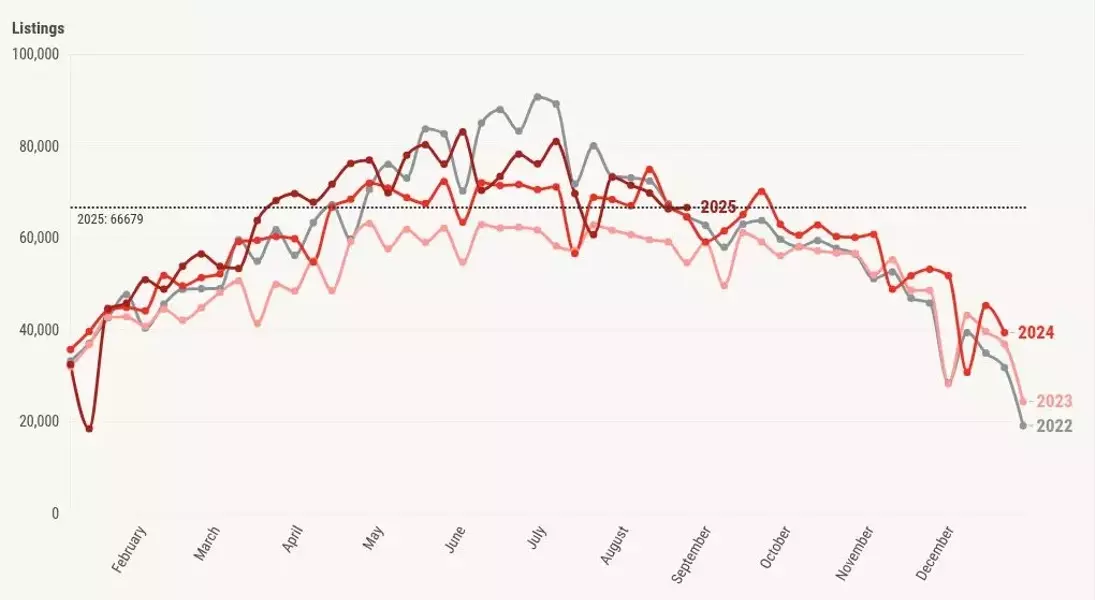
New listings peaked at 83,143 during the week of May 23, 2025, and have since shown a gradual decline. Current trends are below 2022 levels, and a rebound expected last week did not materialize, resulting in negative year-over-year growth. In stark contrast, during the housing bubble crash years, new listings often soared to 250,000-400,000 per week. Last week's new listings stood at 66,679, slightly below 67,476 in 2024.
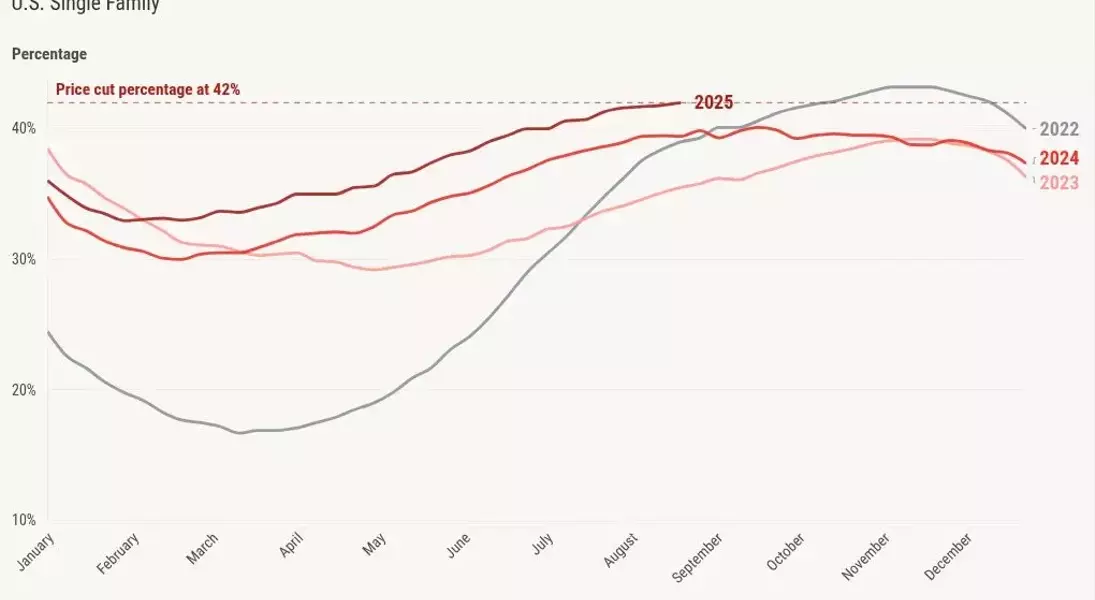
Price reductions, a normal market adjustment, are more prevalent this year (42%) compared to last year (39%), driven by increased inventory and persistent high mortgage rates. This aligns with a cautious 2025 price forecast of a modest 1.77% increase, suggesting negative real home prices. This contrasts with 2024's 4% increase, which defied a 2.33% forecast due to rates falling to around 6% and a subsequent demand surge.
Purchase application data showed a 1% week-over-week growth and a 17% year-over-year gain, with 28 consecutive weeks of positive year-over-year data and 15 consecutive weeks of double-digit growth. If mortgage rates continue their descent below 6.64%, further positive week-to-week data is anticipated.
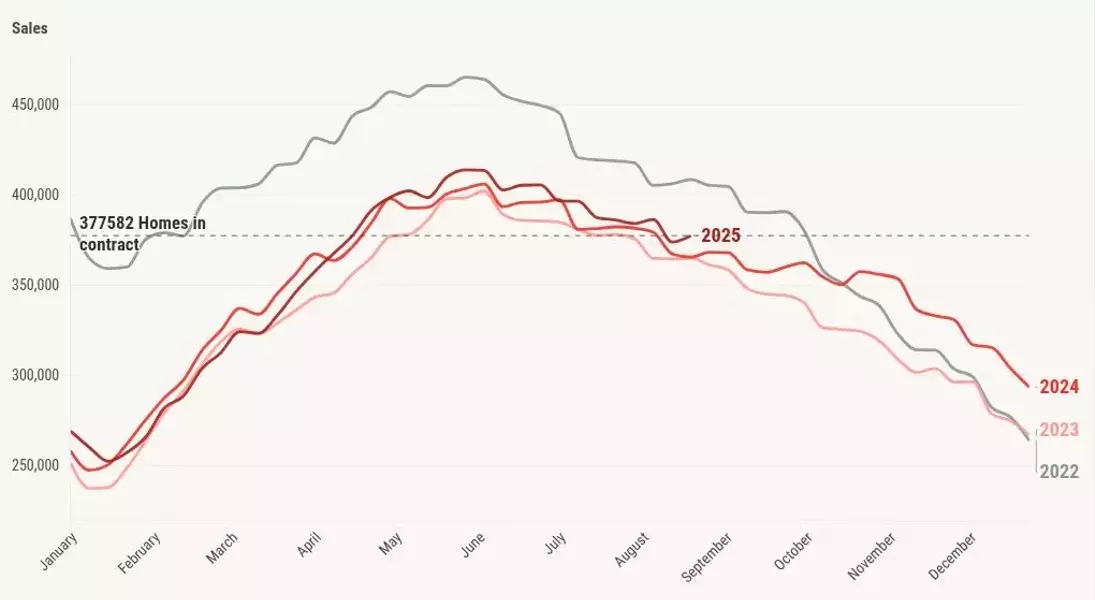
Total pending sales in 2025 reached 377,582, up from 365,944 in 2024. Weekly pending sales slightly increased to 67,173 in 2025 from 66,638 in 2024. These weekly figures serve as leading indicators for future sales data, typically affecting sales within 30-60 days.
Looking ahead, the upcoming week features Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell's speech at the Kansas City Fed's annual Economic Policy Symposium in Jackson Hole, Wyoming. His remarks on recent jobs data versus inflation concerns will be closely watched. Additionally, key housing data releases, including builder confidence, housing starts, and existing home sales, are expected. While this week's reports may not yet reflect the latest mortgage rate lows, an increase in builder confidence is possible. Bond auctions and further Federal Reserve official comments will also shape market sentiment.
The performance of mortgage spreads in 2025 has offered a profound insight into the evolving resilience of the housing market. From a journalistic perspective, this ongoing stability in borrowing costs, despite inflationary pressures, challenges conventional economic wisdom. It underscores the critical importance of less commonly discussed financial mechanisms, like mortgage spreads, in shaping everyday economic realities for millions. This situation compels us to look beyond headline inflation numbers and appreciate the nuanced interplay of financial instruments that ultimately determine market accessibility and affordability. It's a powerful reminder that even in seemingly adverse conditions, underlying market adjustments can create unexpected safeguards, ultimately fostering a more stable environment for housing consumers.
