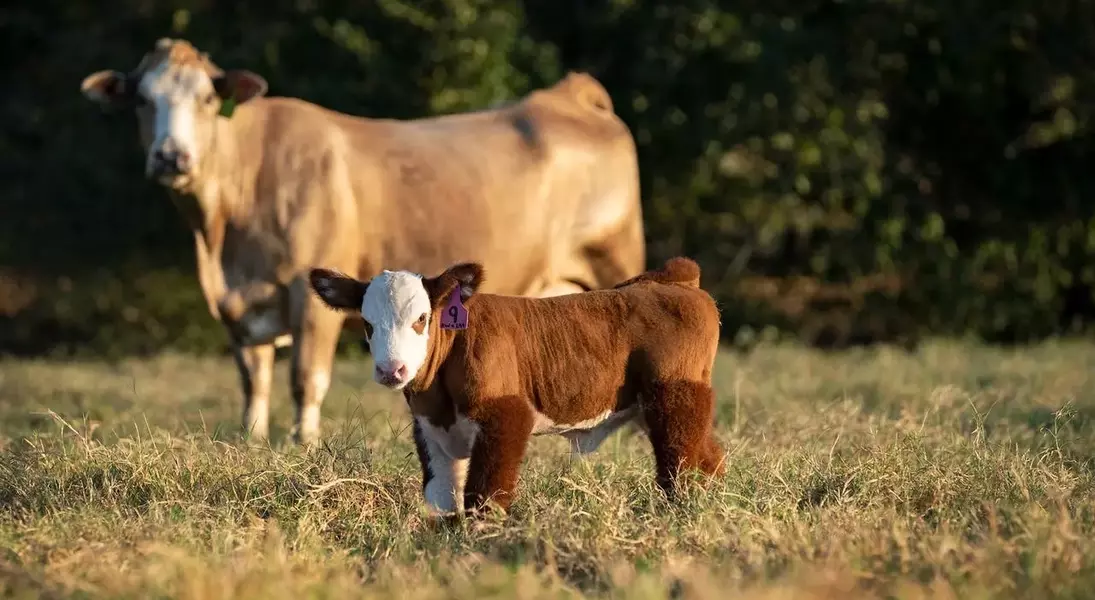



The United States beef market is currently experiencing a period of elevated prices, directly linked to a substantial decrease in the national cattle herd and consistent consumer demand. This situation presents a complex scenario for the industry, as producers are benefiting from record calf sale prices while facing the challenge of rebuilding a herd that reached its lowest point in 73 years. The intricate balance between supply constraints, strong market appetites, and the biological realities of cattle reproduction is shaping the current economic landscape for beef.
Amidst these market conditions, stakeholders are keenly observing the long-term outlook. While immediate profitability incentivizes producers to sell, the need for herd expansion is critical for future stability. The agricultural sector is also contending with varying regional conditions, from drought recovery to pest management, further influencing the overall productivity and supply chain. Understanding these multifaceted elements is crucial for anticipating future trends in the American beef industry.
Current Market Dynamics: High Prices and Low Inventory
The U.S. beef sector is currently defined by a confluence of factors leading to record-high prices across the entire supply chain, from initial sales to retail consumers. This upward trend is primarily attributable to a severe contraction in the national cattle population, which in January 2024 hit a historic 73-year nadir at 28.2 million head, only slightly recovering to 28.7 million. Despite these low numbers, robust consumer demand for beef persists, driving up prices. Cow-calf producers, in particular, are witnessing unprecedented returns on calf sales, a direct consequence of the limited supply meeting unwavering demand. This economic climate is, however, also prompting discussions about its sustainability and the broader implications for the industry's future. The current market snapshot underscores a critical period for beef production, where short-term gains are weighed against long-term strategic adjustments, all while the industry navigates the fundamental principles of supply and demand in a constrained environment.
This unique market situation is not merely a transient phase but a reflection of several interconnected challenges and opportunities within the cattle industry. The historical low in cattle inventory is a direct result of various factors, including prolonged periods of drought in key beef-producing regions like Texas, which severely impacted grazing conditions and forced herd reductions. While producers have attempted to offset lower numbers by feeding cattle to heavier weights, overall beef production remains down year-over-year. The high retail prices, rather than deterring consumers, are met with continued strong demand, indicating beef's inelasticity in the consumer market. This dynamic creates a favorable, albeit potentially unsustainable, environment for ranchers. Experts are examining how long these elevated prices will endure, considering the slow biological cycle of cattle reproduction. The market's current state highlights the delicate balance between environmental challenges, production capacity, and consumer behavior, making strategic planning for herd rebuilding and operational efficiency paramount for long-term stability.
Strategies for Sustainability in Beef Production
The current market conditions, characterized by improved profit margins for cow-calf producers, offer a unique opportunity for strategic re-evaluation within the beef industry, particularly in regions like Texas. With grazing conditions improving and some input costs declining, ranchers are experiencing better profitability. However, this immediate gain often discourages the widespread retention of replacement heifers, which is crucial for increasing the national herd size. While individual producers may choose to hold back heifers to capitalize on future market conditions, the prevailing incentive remains to sell at current record prices. This decision-making paradox underscores the challenge of balancing short-term financial gains with the long-term necessity of herd rebuilding. Anticipating continued upward trends in calf prices, particularly if more producers decide to retain heifers, signals a potential further tightening of supply, which could drive prices even higher. This intricate interplay of economic incentives and biological realities necessitates careful planning for sustainable growth.
In light of these complex dynamics, industry experts strongly advise cow-calf producers to focus on operational efficiencies and optimized profitability, recognizing that the current lucrative period may not last indefinitely. Strategic interventions should encompass improvements in reproductive efficiency, ensuring robust herd health practices, and implementing effective forage management techniques. Furthermore, investing in operational enhancements that reduce long-term costs can bolster resilience against future market fluctuations. Preparing for both favorable and adverse market scenarios is vital, enabling producers to adapt their strategies as conditions evolve. While the present market makes profitability relatively straightforward, the inherent cyclical nature of the beef industry suggests that leaner times will eventually return. Therefore, proactive measures—ranging from genetic selection for improved productivity to advanced nutritional programs—are essential for sustaining profitability and ensuring the long-term viability of beef production in a market increasingly influenced by supply constraints and fluctuating environmental factors.
