

Uncovering the Hidden Costs and Benefits of Circular Construction
Contribution of CE Material Efficiency Strategies to Overall Costs and Benefits
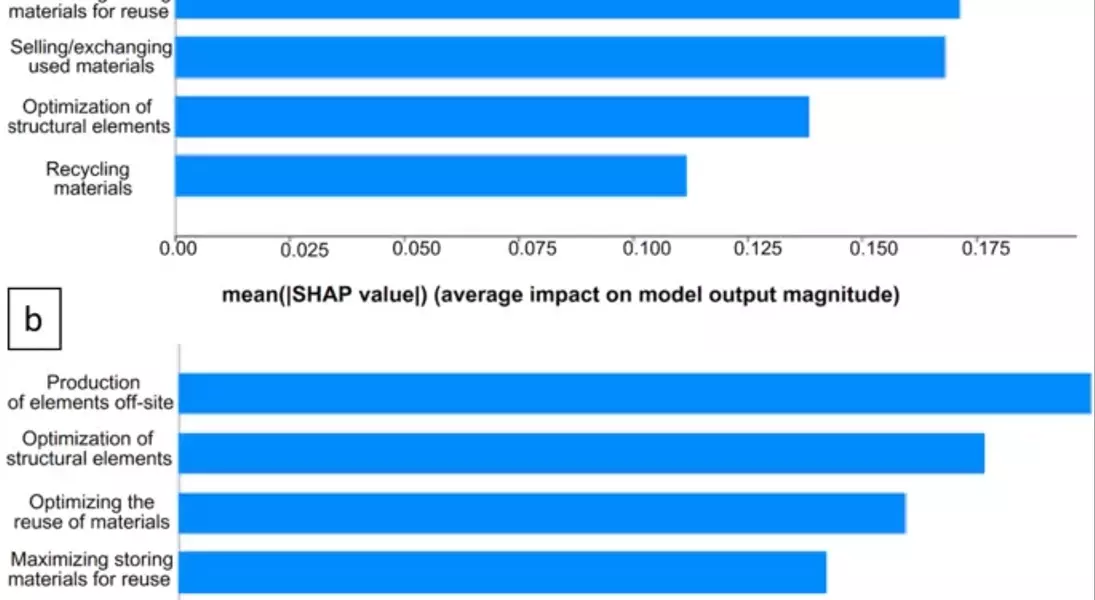
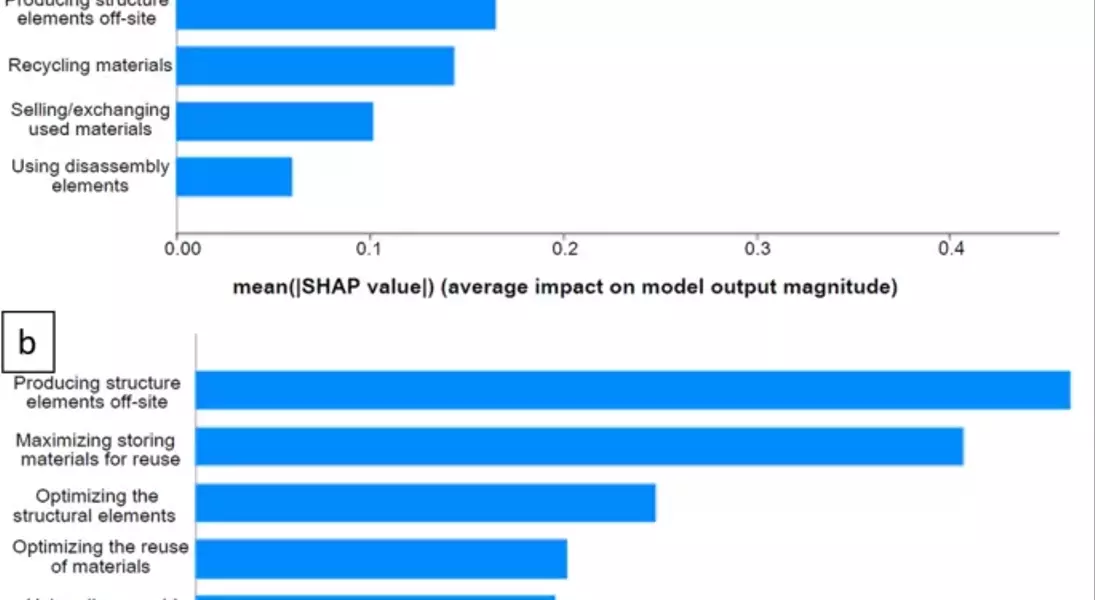
In the studied European countries, optimizing the reutilization of materials, using disassembly elements, and producing elements offsite are identified as the top factors influencing cost increases. While there is some variation within the European cohort, the primary impacts on overall costs remain associated with the recovery of construction materials, disassembly requirements, and offsite production. In non-European countries, similar results appear, with optimizing structural elements replacing 'using disassembly elements' as a top contributor to overall cost increases. Maximizing storage for reuse is also a significant factor in both regions.
Cost reduction can be achieved in the studied European countries by focusing on the reutilization of elements, which stakeholders consider the most significant contributor to overall costs. Other important factors include design for disassembly (DfD) and offsite production of structural elements. In non-European countries, concerns are similar, particularly regarding offsite production and optimizing reuse. However, CE practices are less developed in non-European regions, and the lack of a centralized, non-competitive recycling model may lead to recycling being seen as a less significant contributor to overall costs.
Cost Drivers and Benefits of CE Material Efficiency Strategies
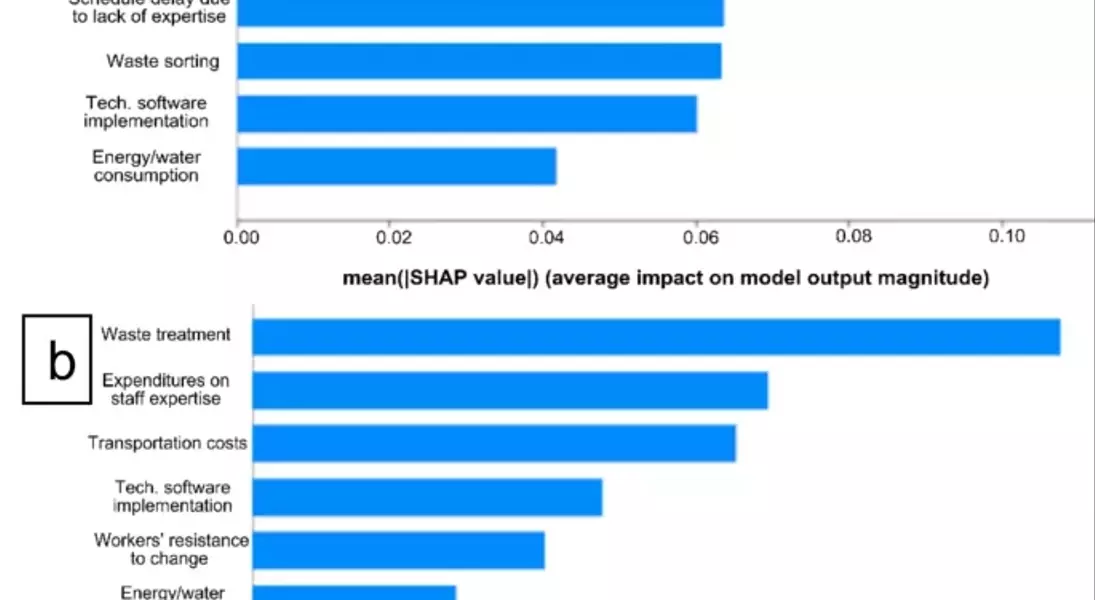
Within the studied European countries, regulatory non-compliance resulting in fines and penalties is a top cost driver. Reduced work efficiency due to workers' resistance to change also significantly impacts overall expenses, along with maintenance costs and workflow disruptions. In non-European countries, waste treatment costs stand out, potentially indicating less-developed waste management infrastructure. Both regions face challenges in managing human factors in CE implementation, such as resistance to change, which affects work efficiency.
The findings also show differences in the significance of various factors between European and non-European countries. For example, non-compliance costs are a primary concern in Europe, while waste sorting was considered less important in this research but is gaining more attention. In non-European countries, stakeholders are concerned about expenditures related to staff expertise and transportation costs. By understanding these differences, targeted approaches can be developed to support CE implementation.
The results highlight the importance of adapting waste management strategies to each region's specific circumstances and priorities. By identifying potential risks and opportunities and considering stakeholder interests, governments and funding institutions can refine regulations and create incentives to support the implementation of circular economy principles in the construction sector.
