


Moltbot, previously known as Clawdbot, is gaining considerable attention for its ambitious claims of automating a wide array of personal and business tasks. This artificial intelligence assistant aims to streamline daily operations by integrating with existing chat applications like WhatsApp and Telegram, allowing users to manage everything from email inboxes and calendars to flight check-ins and even business development. However, these enticing capabilities come hand-in-hand with serious security and privacy concerns that warrant careful consideration before adoption.
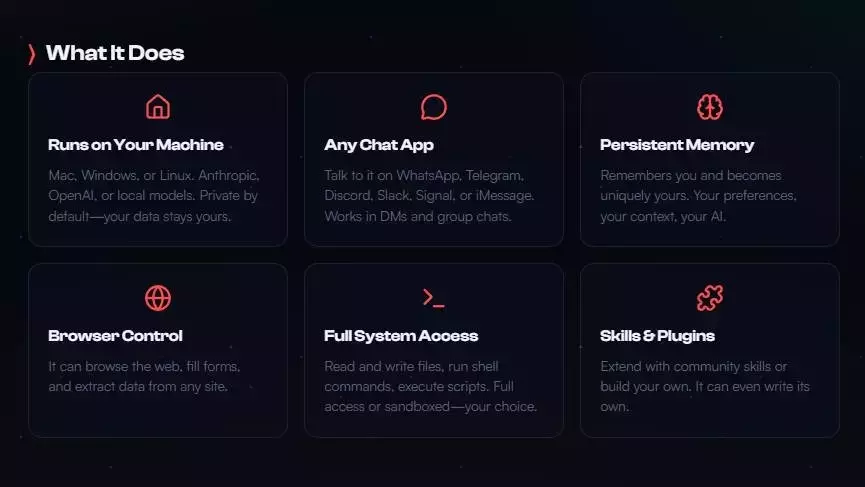
The AI's developers were compelled to rebrand from Clawdbot to Moltbot due to trademark conflicts with Anthropic, the creators of Claude. Despite the name change, Moltbot maintains its core mission: to be a proactive AI that executes tasks rather than merely providing information. Its marketing highlights the potential for significant productivity gains, positioning it as a virtual employee capable of performing routine administrative duties and even generating business insights. This vision has sparked considerable interest, as evidenced by a temporary surge in Cloudflare's stock, whose content delivery networks were perceived as beneficial for supporting Moltbot's functionality.
A key appeal for some users, particularly those with a focus on data control, is Moltbot's ability to run locally on a chosen device or cloud server. It stores its operational 'memory' persistently in Markdown format, offering a degree of user oversight. However, this local operation primarily pertains to the bot's interface and data storage, while the core AI processing often relies on external large language models (LLMs) and their associated subscriptions. The setup process involves configuring command-line parameters and integrating various AI service tokens, as well as connections to other applications, all managed through a dedicated Control User Interface.
Despite the sophisticated functionality, the practical implications and potential pitfalls of Moltbot have been a subject of ongoing discussion. While enthusiasts envision the AI as a diligent employee handling complex tasks such as market trend analysis, content creation, and business management, cybersecurity experts are sounding alarms. One significant vulnerability identified by security researchers, like Jamieson O'Reilly, is the exposure of Moltbot Control UIs through web traffic scrapers. While many visible instances may not be directly exploitable, the existence of misconfigured systems presents a clear risk.
Moreover, the inherent nature of LLMs introduces a more profound security challenge: prompt injection. This phenomenon occurs when an AI struggles to differentiate between legitimate user commands and malicious data embedded within seemingly innocuous inputs. This susceptibility could lead to the AI executing unintended actions or inadvertently leaking sensitive information. Cybersecurity experts, such as Low Level, highlight that even seemingly simple external inputs, like an email, could be manipulated to trick Moltbot into performing unauthorized functions, such as playing music on a connected device or revealing calendar details, as demonstrated with other AI models like Google Gemini. Such incidents underscore the critical need for robust security measures and a cautious approach to granting AI systems extensive access to personal and professional data.
Given these security complexities, the current narrative surrounding Moltbot as a beginner-friendly tool for instant productivity gains is misleading. While its capabilities are undeniably impressive and represent a significant leap in AI automation, the technical expertise required to secure and effectively manage such a system is substantial. Until developers can comprehensively address vulnerabilities like prompt injection and provide more intuitive security configurations, the widespread adoption of AI agents with broad system access may remain limited to those with a deep understanding of cybersecurity and AI intricacies. The long-term viability and utility of Moltbot will depend heavily on its evolution towards a more secure and user-friendly platform, bridging the gap between its powerful potential and the practical realities of digital security.
