


Google's Chrome browser is set to receive a significant upgrade with the introduction of new artificial intelligence functionalities, prominently featuring the 'Auto Browse' tool. This innovative function is promoted as a 'powerful agentic experience' capable of independently managing various multi-step online activities, offering users a more streamlined browsing experience. While designed to enhance efficiency in daily digital tasks, its comprehensive capabilities also prompt considerations regarding user control and the intricacies of automated decision-making.
This advancement in Chrome's AI capabilities signifies a shift towards more proactive and intelligent web interaction. By leveraging the power of AI, Google aims to reduce the manual effort involved in routine online chores, transforming the browser into a more sophisticated personal assistant. However, the extent of this automation and the implications for user interaction remain key points of discussion as this new feature rolls out.
The Promise of Effortless Digital Assistance
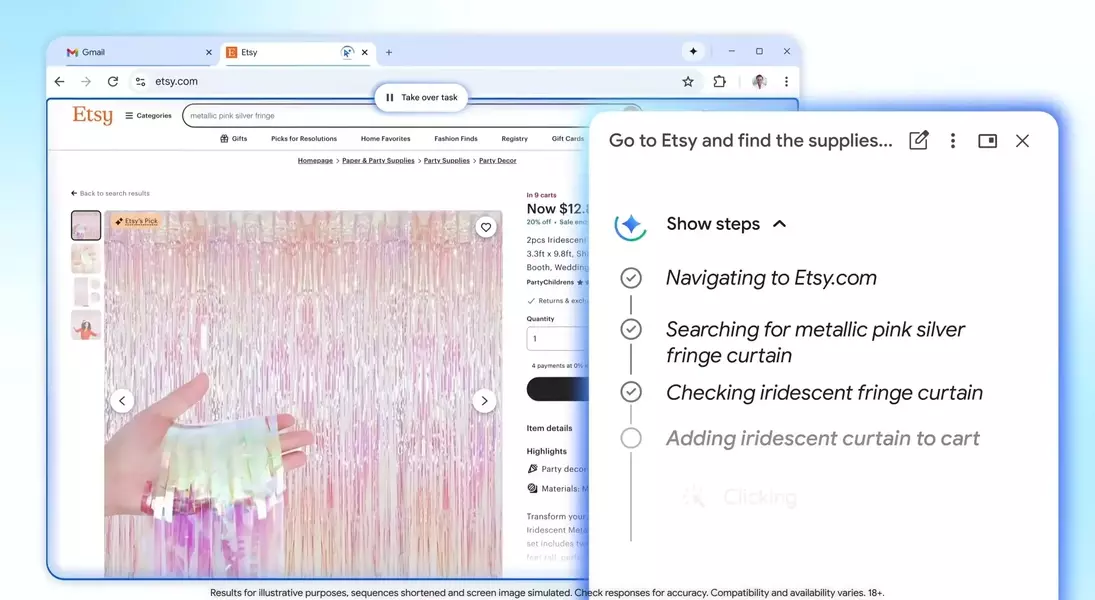
Google is rolling out a new 'auto browse' feature in Chrome, hailed as a 'powerful agentic experience' that promises to simplify complex online tasks. This AI-driven tool extends beyond traditional autofill, aiming to manage multi-step processes on behalf of the user. For instance, it can optimize vacation planning by researching flight and hotel prices across various dates, offering budget-friendly options and significantly reducing the tedious comparison work involved. This capability is expected to alleviate common frustrations associated with online booking and similar time-consuming activities.
The potential applications of 'auto browse' are vast, with testers reporting success in scheduling appointments, completing lengthy online forms, compiling tax documents, obtaining service quotes from plumbers and electricians, managing subscriptions, and even renewing driving licenses. These examples highlight the feature's capacity to tackle mundane yet essential administrative chores, thereby freeing up users' time and mental energy. The system is designed to intelligently navigate web pages, extract relevant information, and perform actions that would typically require considerable manual input, thus transforming the browser into a highly efficient personal assistant for everyday digital life.
Navigating the Complexities of Automated Web Interactions
Despite the significant advantages offered by 'auto browse', the expansive nature of its capabilities also gives rise to important considerations regarding accuracy and user oversight. The system's ability to identify items from images, search for similar products, and even apply discount codes while adhering to a budget presents both convenience and potential pitfalls. For example, relying on AI to interpret visual cues for purchasing decisions could lead to unintended outcomes if the AI's understanding deviates from the user's precise intent or if visual information is ambiguous. Such advanced automation requires a delicate balance to prevent over-eager or misdirected actions by the AI.
To mitigate concerns about autonomous decision-making, Google has implemented safeguards that ensure users retain ultimate control over critical actions. 'Auto browse' is designed to pause at crucial junctures, such as before finalizing a purchase or posting content on social media, requiring explicit user confirmation. This interactive design allows users to review and approve significant steps, thereby preventing unwanted transactions or public disclosures. The integration of Google Password Manager, with user permission, further enhances the feature's utility for tasks requiring logins while maintaining a layer of security and user consent, striving to create a robust yet accountable automated browsing experience.
