


An extensive survey conducted across five countries—Australia, Canada, Mexico, the United Kingdom, and the United States—has revealed significant variations in the use of online food retail platforms. The study examined how demographic and behavioral factors influence the adoption of these services. Among the findings, Mexico emerged as the leader in online restaurant and convenience store orders, while the U.S. showed a preference for online grocery shopping and meal kits. Additionally, younger generations, particularly Millennials and Generation Z, demonstrated a higher likelihood of using these platforms compared to older age groups.
Detailed Insights into Online Food Retail Adoption Across Nations
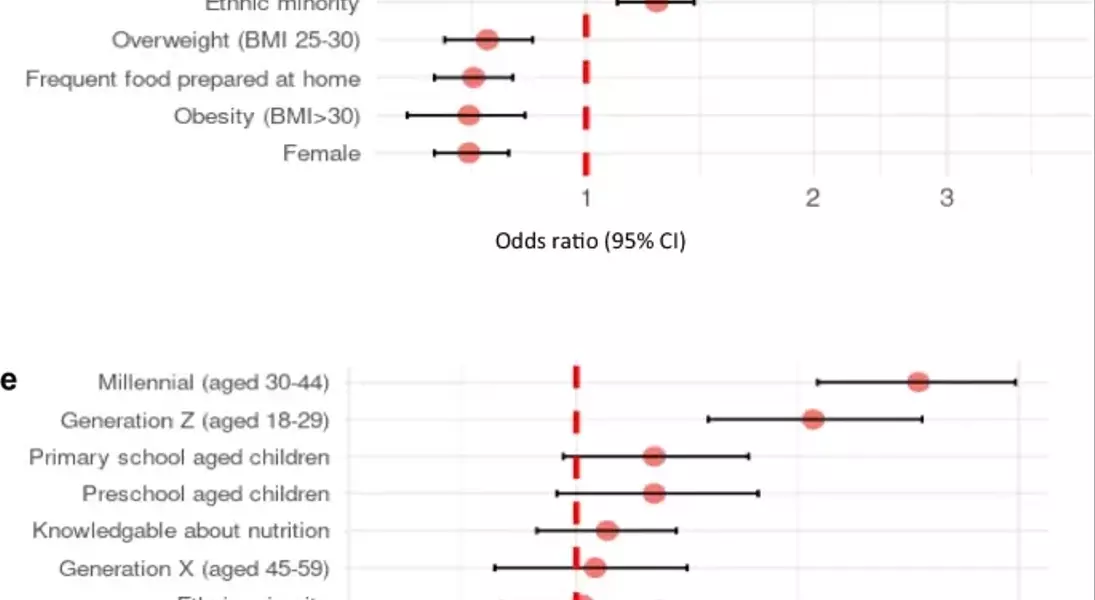
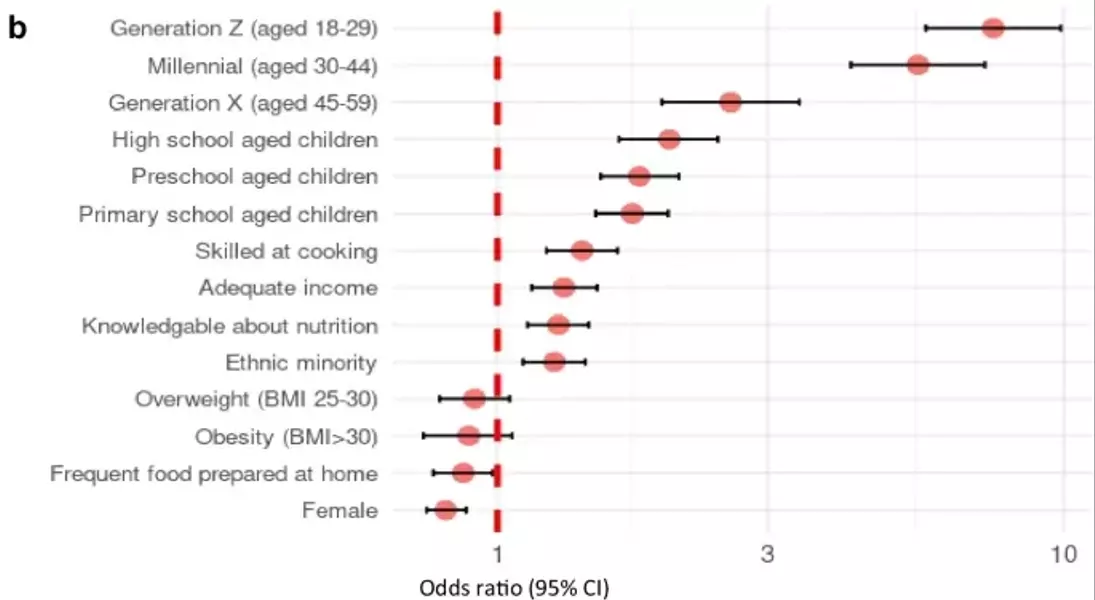
In a comprehensive analysis of online food retail usage, researchers uncovered striking differences among nations. In Mexico, nearly three-quarters of respondents reported ordering meals online, reflecting a robust digital commerce culture. Conversely, Canada lagged behind its counterparts in embracing these technologies. Key demographics influencing platform adoption included gender, with men more inclined toward online restaurant orders, and household composition, where families with primary school-aged children favored online supermarket services.
The study further highlighted that individuals identifying as ethnic minorities were more likely to utilize online food retail platforms. Economic factors also played a crucial role; those perceiving their income as adequate exhibited greater engagement with various online food services. Moreover, participants who considered themselves knowledgeable about nutrition and skilled in cooking showed increased odds of making online grocery purchases.
From an international perspective, the prevalence of online food ordering was notably higher in Mexico and the United States compared to Australia, Canada, and the UK. This disparity could be attributed to differing technological infrastructures and consumer preferences within each country. For instance, in regions lacking access to fresh produce, such as certain areas in the U.S., online grocery retailers provided essential alternatives for residents.
Younger generations, characterized by their affinity for technology and willingness to experiment with new conveniences, led the charge in adopting online food retail platforms. Their behavior contrasted sharply with that of older adults, who remained largely traditional in their purchasing habits. Furthermore, the increasing popularity of meal kit delivery services underscored a growing demand for convenient yet healthy meal options among tech-savvy consumers.
Journalists and policymakers alike should take note of these trends, as they highlight both opportunities and challenges in shaping healthier dietary choices through digital means. As societies continue to evolve alongside technological advancements, ensuring equitable access to nutritious foods via online platforms becomes paramount.
This research underscores the importance of understanding diverse user profiles when designing effective public health strategies aimed at promoting better eating habits globally. By leveraging insights gained from studies like this one, stakeholders can work collaboratively towards creating supportive environments conducive to good health and well-being.
As we delve deeper into the implications of widespread online food retail usage, it becomes evident that fostering awareness around nutritional content on digital platforms is vital. Policymakers must collaborate closely with industry leaders to implement measures ensuring transparency in product information, thereby empowering consumers to make informed decisions regarding their diets. Ultimately, addressing potential disparities in access to quality food sources remains critical in advancing global efforts against rising obesity rates and related non-communicable diseases.
