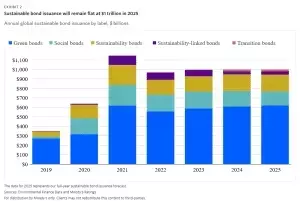
The global sustainable bond market is poised for another year of steady issuance at approximately $1 trillion in 2025, underscoring its resilience despite political shifts and heightened scrutiny. This article delves into the drivers behind this stability, exploring the diverse sectors and regions shaping the future of sustainable finance.
Driving Investment Toward a Greener Tomorrow
Green Bonds: Pioneering Clean Energy Solutions
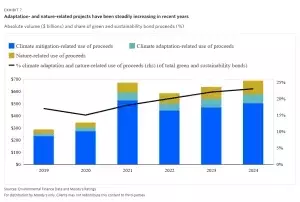
Green bonds are set to lead the charge in 2025, with an anticipated issuance of $620 billion. This remarkable figure reflects a growing commitment to climate mitigation, bolstered by policy support, private sector engagement, and advancements in clean energy technologies. The decline in costs associated with renewable energy has made green bonds an increasingly attractive option for investors seeking impactful returns. Moreover, there is a notable shift towards financing adaptation projects as the economic and human toll of extreme weather events continues to rise. Investments in resilient infrastructure, water-efficient data centers, and emerging green technologies for hard-to-abate sectors are expected to further drive green bond volumes. Additionally, nature-related projects are gaining momentum, driven by a heightened focus on ecosystem conservation and biodiversity preservation.Social and Sustainability Bonds: Balancing Social Impact
While social bond issuance is projected to decline by 9% to $150 billion in 2025, it remains significantly higher than pre-pandemic levels, highlighting sustained interest in social initiatives. These bonds have played a crucial role in addressing societal challenges, from healthcare to education. Sustainability bonds, which fund a mix of green and social projects, are forecasted to remain stable at $175 billion. This segment's steady growth over the past decade underscores the importance of diversified funding sources in achieving comprehensive sustainability goals.Transition and Sustainability-Linked Bonds: Emerging Opportunities
Transition bonds, introduced in 2024 with Japan’s $11 billion issuance, are expected to hold steady at $20 billion in 2025. Although currently dominated by Japan, this niche market shows potential for diversification as more issuers adopt transition finance strategies to achieve low-carbon goals. Sustainability-linked bonds (SLBs) could see a modest 14% growth to $35 billion. However, investor scrutiny over the robustness of SLB targets remains a challenge. Despite this, SLBs offer an alternative for issuers without immediate capital investment needs for green or social projects.Regional Dynamics: Varying Trajectories
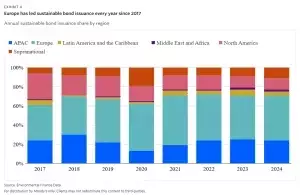
The sustainable bond market in 2025 will exhibit divergent trends across regions, influenced by political, economic, and regulatory factors. Europe, as the leading region for sustainable bond issuance since 2017, is projected to maintain its dominance with $465 billion in volumes. The implementation of the European Green Bond Standard may further accelerate growth.In contrast, APAC’s issuance is forecasted at $238 billion, slightly below 2024 levels. Transition finance remains a key focus, supported by government initiatives and sustainable finance policies. North America, however, faces muted prospects, with 2024 volumes totaling $124 billion—a 30% decline from 2021. Reduced federal investment in clean energy under the new administration is partly offset by private-sector initiatives and state-level efforts.Latin America and the Caribbean could witness a rebound, driven by COP30 in Brazil and increased regional activity. Large sovereign issuances and the momentum from the COP summit will likely boost volumes. In the Middle East and Africa, while accounting for the smallest share of issuance, the focus on clean energy investments and carbon transition risks supports long-term growth.Climate Financing: Catalyzing the Green Transition
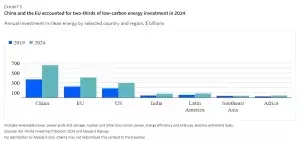
Climate financing plays a pivotal role in addressing global energy needs and accelerating the green transition. Policy support, private-sector pledges, and declining costs of clean energy technologies continue to drive climate investments. Despite potential setbacks, many nations are committed to meeting decarbonization and energy security objectives.China and the EU, responsible for 66% of global clean energy investment in 2024, are spearheading efforts in renewable power, energy efficiency, and low-emissions technologies. Emerging markets face significant climate finance challenges, with annual funding needs exceeding $1 trillion. However, increased investments from advanced economies, multilateral development banks, and innovative financing solutions could drive a rebound in EM sustainable bond issuance in 2025.Expanding Frameworks for a Greener Future
As public and private issuers embrace adaptation and resilience projects, sustainable bond frameworks are expanding. For instance, the Netherlands’ green bond framework funds long-term flood management strategies. Similarly, U.S. utilities are investing in grid resilience to address wildfire risks, integrating these initiatives into their bond frameworks. Nature-focused financing is also gaining traction, with blue bonds supporting marine and coastal projects like kelp forest cultivation for carbon sequestration.